Ecommerce, or electronic commerce, is the process of buying and selling goods and services over the internet. It involves the exchange of products or services between businesses, consumers, or both. Ecommerce business is facilitated through platforms such as websites, mobile apps, or online marketplaces.
E-commerce is a transaction of buying or selling online. Electronic commerce draws on technologies such as mobile commerce, electronic funds transfer, supply chain management, Internet marketing, online transaction processing, electronic data interchange (EDI), inventory management systems, and automated data collection systems.
Modern electronic commerce typically uses the World Wide Web for at least one part of the transaction's life cycle although it may also use other technologies such as e-mail. Typical e-commerce transactions include the purchase of online books such as Amazon & music purchases Spotify
There are three areas of e-commerce:
(i) Online retailing
(ii) Electric markets, and
(iii) Online auctions E-commerce is supported by electronic business
Nature of E- Commerce
It has also been described as a "fusion of telecommunications and computing technology to conduct business. That is the creation and management of relationships between buyers and sellers, facilitated by an interactive and pervasive electronic medium". Some of the main reasons for the increase in electronic trading are:-
(I) The drive to reduce the costs
(Il) Easy accessibility to the Internet
(III) The lack of regulation on the Internet
(IV) Access to global markets for vendors
(V) Greater choice and potentially lower prices for purchasers
(VI) Lower inventory costs for vendors
Examples of E-Commerce
Ecommerce can take on a variety of forms involving different transactional relationships between businesses and consumers, as well as different objects being exchanged as part of these Transaction.
- Retail: The sale of a product by a business directly to a customer without any intermediary.
- Wholesale: The sale of products in bulk, often to a retailer that then sells them directly to consume
- Drop shipping: The sale of a product. which is manufactured and shipped to the consumer by a third party.
- Crowdfunding: The collection of money from consumers in advance of a product being available in order to raise the startup capital necessary to bring it to market.
- Subscription: The automatic recurring purchase of a product or service on a regular basis until the subscriber chooses to cancel.
- Physical products: Any tangible good that requires inventory to be replenished and orders to be physically shipped to customers as sales are made.
- Digital products: Downloadable digital goods, templates, and courses, or media that must be purchased for consumption or licensed for use.
- Services: A skill or set of skills provided in exchange for compensation. The service provider's time can be purchased for a fee.
Advantages of E-commerce
There are many advantages to e-commerce, including:
- Increases Sales and Revenue : E-commerce always helps to increase sales and revenue as it widens the market by reaching out to new customers. It also allows businesses to offer discounts and incentives that are not possible in a physical store. There are also many opportunities for cross-selling and up-selling.
- Reduces Costs : E-commerce also helps reduce business costs as it eliminates the need for a physical store and sales staff. It also reduces inventory costs and transportation costs. There are also many opportunities for cost-saving through online auctions and supply chains.
- Eliminates Geographic Barriers : E-commerce also eliminates geographic barriers, as customers can buy goods and services from anywhere in the world. This allows businesses to sell to new markets and expand their customer base. It may also help to reduce the cost of doing business.
- Improves Customer services : This is because e-commerce allows businesses to offer 24/11 customer service, which is not possible in a physical store. It also allows customers to compare prices and products from different retailers easily. Sometimes there are also additional services, such as customer reviews and ratings, that are not available in a physical store.
- Increases Efficiency : Efficiency is increased as orders can be placed and processed quickly and easily through an e-commerce website. This eliminates the need for paperwork and reduces the chances of human error. It also allows businesses to track inventory levels and sales trends in real-time.
Disadvantages of E-commerce
However, there are also some disadvantages to e-commerce, including:
- Lack of Social Interaction : One disadvantage is that there is a lack of social interaction, as people cannot see or touch the product before they buy it. This may lead to dissatisfaction with the purchase if the product is not what was expected.
- Security Risks : Another disadvantage is that there are security risks, as sensitive financial information can be stolen by hackers. This can result in loss of money and identity theft. There may also be risks involved with buying and selling products online, as there is no guarantee of product quality or authenticity.
- Difficulties with Returns : Another disadvantage is that it can be difficult to return products that have been bought online. This is because businesses often require the product to be returned in its original packaging, which may not be possible if the product has been used. There may also be shipping costs involved in returning the product.
- Lack of Trust : There may be a lack of trust among consumers when it comes to buying goods and services online. This is because they may be afraid of being scammed or not receiving the product that they ordered.
Reasons for Online Transactions
1. Convenience
• Online transactions allow users to make payments, transfer funds, and purchase goods or services from anywhere, without the need to visit a bank or a store.
• Available 24/7, eliminating the limitations of working hours in physical banking.
Example:
A person can pay utility bills, mobile recharge, or book tickets from the comfort of their home using online banking or payment apps.
2. Speed & Efficiency
• Transactions happen almost instantly, unlike traditional banking, which may take hours or even days.
• Reduces the need for paperwork and manual processing.
Example:
Transferring money through UPI (Unified Payments Interface) happens within seconds compared to traditional bank transfers, which may take longer.
3. Security
• Online banking systems use encryption, OTPs (One-Time Passwords), and two-factor authentication to ensure secure transactions.
• Digital payments reduce the risk of carrying cash, which can be lost or stolen.
Example:
Banks and payment apps like PayPal, Google Pay, and Paytm provide fraud detection systems to protect users from unauthorised transactions.
4. Wide Accessibility
• Online transactions enable financial inclusion, allowing people in remote areas to access banking services.
• Supports cross-border transactions, making international payments easier.
Example:
A freelancer in India can receive payments from a client in the USA through PayPal or wire transfer without visiting a bank.
5. Cost Savings
• Online transactions reduce costs related to physical banking, such as fuel, transport, and time spent standing in long queues.
• Many online banking services offer lower transaction fees compared to traditional methods.
Example:
Banks often charge lower fees for NEFT, IMPS, or UPI transfers compared to demand drafts or physical money transfers.
6. Record Keeping & Transparency
• Digital transactions generate automated receipts and transaction history, making it easy to track spending and maintain financial records.
• Businesses benefit from detailed transaction logs for accounting and auditing purposes.
Example:
An individual can check their bank statement online to verify past transactions instead of relying on printed passbooks.
7. Contactless Transactions
• During health crises like the COVID-19 pandemic, online payments helped reduce physical contact and the spread of infections.
• Safer than handling cash, which can carry germs.
Example:
Supermarkets and restaurants now widely accept QR code payments, allowing customers to pay without touching cash or credit cards.
8. Multiple Payment Options
• Online transactions provide flexibility by supporting debit/credit cards, UPI, e-wallets, net banking, and cryptocurrencies.
• Customers can choose the most convenient method based on their preference.
Example:
While shopping online, a customer can choose to pay via Google Pay, Paytm, credit card, or even “Cash on Delivery” based on their convenience.
9. Automated Payments & Subscriptions
• Users can set up auto-debit for bill payments, insurance premiums, and EMIs to avoid missing due dates.
• Subscription-based services like Netflix, Amazon Prime, and Spotify rely on recurring online transactions.
Example:
A user can schedule monthly rent payments through their banking app, ensuring timely payments without manual intervention.
10. Real-Time Notifications & Fraud Prevention
• Banks and payment apps send instant alerts via SMS and email for every transaction, ensuring transparency.
• Customers can immediately report suspicious activity and block their accounts if needed.
Example:
If a fraudulent transaction occurs, the user gets a real-time alert and can immediately block their card or account using online banking.
Electronic Commerce (E-Commerce) and Its Types
Electronic commerce (E-commerce) refers to the process of buying and selling goods, services, and information over the internet. It enables businesses and consumers to engage in transactions through online platforms, eliminating the need for physical presence. E-commerce has revolutionised traditional business models by making transactions more efficient, cost-effective, and accessible on a global scale.
Types of E-Commerce
1. Business-to-Consumer (B2C) E-Commerce
B2C e-commerce is the most common type, where businesses sell products or services directly to individual consumers. It includes online retail stores like Amazon, Flipkart, and Myntra, as well as streaming services such as Netflix and Spotify.
Key Features:
• Allows consumers to shop anytime and from anywhere.
• Uses AI-driven recommendations to enhance the shopping experience.
• Includes categories like online shopping, food delivery, and digital subscriptions.
Challenges:
• High competition among online retailers.
• Issues like cybersecurity threats and logistics management
2. Business-to-Business (B2B) E-Commerce
B2B e-commerce involves transactions between businesses, such as manufacturers selling to wholesalers or wholesalers supplying retailers. Platforms like Alibaba and IndiaMART facilitate bulk trade between companies.
Key Features:
• Deals with large orders and long-term business relationships.
• Helps businesses reduce procurement costs through bulk purchases.
Challenges:
• Requires strong supply chain management.
• Complex negotiation and approval processes.
3. Consumer-to-Consumer (C2C) E-Commerce
C2C e-commerce enables individuals to sell products to other consumers, often through third-party platforms like OLX, Quikr, and eBay. People use these platforms to sell second-hand or handmade products.
Key Features:
• Facilitates peer-to-peer selling without intermediaries.
• Includes auction-based sales and direct transactions.
Challenges:
• Risk of scams and fraudulent listings.
• Lack of standardised return policies.
4. Consumer-to-Business (C2B) E-Commerce
C2B e-commerce occurs when individuals offer products or services to businesses. This model is common in freelancing, influencer marketing, and digital content sales. Platforms like Upwork, Fiverr, and Shutterstock allow individuals to sell their skills or creative work to businesses.
Key Features:
• Gives individuals opportunities to earn online.
• Provides businesses access to a wide talent pool.
Challenges:
• High competition among freelancers.
• Payment disputes and quality assurance issues
5. Business-to-Government (B2G) E-Commerce
B2G e-commerce involves businesses providing goods or services to government agencies. Governments use digital platforms like GeM (Government e-Marketplace) in India and SAM.gov in the U.S. for procurement and contract bidding.
Key Features:
• Ensures transparency in government purchases.
• Involves contracts for IT services, infrastructure, and office supplies.
Challenges:
• Long approval processes for tenders.
• Strict regulatory compliance requirements.
6. Consumer-to-Government (C2G) E-Commerce
C2G e-commerce refers to online interactions between individuals and government agencies. This includes services like online tax payments, bill payments, and applications for official documents (passports, driver’s licenses).
Key Features:
• Saves time by reducing paperwork and physical visits.
• Improves government service efficiency through digital transactions.
Challenges:
• Digital literacy barriers for some users.
• Cybersecurity risks and occasional technical glitches.
7. Mobile Commerce (M-Commerce)
M-commerce refers to e-commerce conducted via mobile devices such as smartphones and tablets. Popular examples include shopping apps (Amazon, Flipkart), mobile payment services (Google Pay, Paytm), and food delivery apps (Zomato, Swiggy).
Key Features:
• Provides convenience and faster transactions.
• Uses AI-driven recommendations for a personalised experience.
Challenges:
• Security risks in mobile transactions.
• Dependence on stable internet connectivity.
8. Social Commerce (S-Commerce)
Social commerce involves buying and selling products through social media platforms. Businesses use platforms like Facebook Marketplace, Instagram Shops, and Pinterest Buyable Pins to reach customers directly.
Key Features:
• Integrates online shopping with social media engagement.
• Uses influencer marketing and customer reviews for brand promotion.
Challenges:
• Trust concerns due to unverified sellers.
• Limited payment and refund options compared to traditional e-commerce.
Electronic Commerce Models
1. Business-to-Consumer (B2C)
The B2C model involves businesses selling products or services directly to individual consumers. It is the most common form of e-commerce, where customers browse, compare, and purchase items through online platforms. E-commerce websites such as Amazon, Flipkart, and Myntra operate under this model, offering a wide range of products like electronics, clothing, and groceries with home delivery and secure payment options.
2. Business-to-Business (B2B)
In the B2B model, transactions take place between businesses rather than individual consumers. Manufacturers, wholesalers, and retailers engage in bulk purchasing with negotiated pricing. These transactions often involve long-term contracts and require secure supply chain management. Platforms like Alibaba, IndiaMART, and SAP Ariba connect businesses for wholesale trade, ensuring efficiency in procurement and distribution.
3. Consumer-to-Consumer (C2C)
The C2C model enables individuals to sell products or services to other individuals using third-party platforms. This model is commonly used for selling second-hand goods, collectibles, or handmade items. Websites like OLX, eBay, and Facebook Marketplace provide a space for consumers to list, buy, and sell items without the involvement of a traditional business entity.
4. Consumer-to-Business (C2B)
In the C2B model, individuals offer products or services to businesses. This is common in freelancing, crowdsourcing, and influencer marketing, where individuals provide expertise, reviews, or promotional services to companies. Platforms like Upwork, Fiverr, and Freelancer allow professionals such as graphic designers, content writers, and IT consultants to connect with businesses seeking specialised skills.
5. Business-to-Government (B2G) / Business-to-Administration (B2A)
The B2G or B2A model involves businesses providing goods and services to government agencies or public institutions. Governments use e-commerce platforms for procurement, licensing, and regulatory processes. India’s Government e-Marketplace (GeM) is an example of an online platform where businesses bid for government contracts, ensuring transparency in public sector procurement.
6. Consumer-to-Government (C2G) / Consumer-to-Administration (C2A)
In the C2G or C2A model, individuals interact with government agencies online for various services. This includes paying taxes, applying for official documents, or making utility payments. Platforms like online tax portals, passport application websites, and bill payment services allow citizens to access government services conveniently from their homes.
Challenges & Barrier in E-Commerce Environment
1. Intense competition
The ease of starting and managing eCommerce businesses has also led to a multitude of competitors vying for the attention and loyalty of customers. The digital marketplace is saturated with numerous online stores offering similar products and services, making it challenging to stand out from the crowd.
By crafting a unique value proposition and differentiating your brand with on-time delivery, understanding target audience needs, and experiences will ensure competition is overcome.
2. Customer Acquisition
Acquiring new customers is a constant challenge in the eCommerce industry. With countless online stores competing for customer attention, businesses must employ effective strategies to attract and convert potential buyers.
Using digital marketing tactics, search engine optimisation (SEO), social media advertising, influencers, and targeted content marketing that emphasises your value proposition will lead to better customer acquisition.
3. Abandoned Shopping Cart
One of the significant hurdles faced by eCommerce businesses is the issue of abandoned shopping carts. Customers often add items to their carts but do not complete the purchase because of various reasons. The reasons may include complicated or time-consuming checkout processes, concerns about payment security, unexpected costs, or distractions during the shopping journey.
You can solve this challenge by displaying trust-inducing icons of secure payment gateways, following up with personalised emails, and incentivising a successful transaction. Integrating your services with secure third-party logistics providers can also ensure carts are not abandoned.
4. Limitations in Website Performance
The performance of an eCommerce website plays a crucial role in shaping the customer experience. Slow-loading pages, technical glitches, or unresponsive interfaces can frustrate visitors and lead to abandoned shopping sessions.
To address these challenges, it is essential to consider switching to a reliable hosting provider, implementing website optimisation techniques, and conducting regular performance testing for your site.
5. Lack of Mobile-friendliness
With the increasing dominance of mobile devices in online shopping, businesses must adapt their eCommerce platforms to cater to mobile users effectively.
Optimise your website for the mobile user, ensuring its responsive design and intuitive navigation offer a streamlined checkout process using a mobile app to give customers a better experience.
6. Unoptimized Inventory
Managing inventory efficiently is crucial in eCommerce. Unoptimised inventory can lead to issues like stockouts or excess stock, resulting in lost sales or increased carrying costs.
Integrating with automated platforms of shipping and logistics providers enables you to track stock levels, automate reordering, and gain real-time visibility into your inventory. Forecast demandwith precision, and let the light of optimised inventory levels guide your path.
7. Logistics Gaps
Your eCommerce business is greatly impacted if your shipping and logistics providers are unreliable and cannot deliver as per the timeline your business offers. Poor performance and repeated delays will lead to customer churn, even if you have a great product portfolio.
To overcome these challenges, it is crucial to effectively manage the delivery of diverse products and handle suppliers, manufacturers, and international customers. Negotiate favourable rates with these providers and offer flexible shipping options to secure customer loyalty.
8. Poorly-framed Returns and Refunds Policies
A challenging aspect of eCommerce is managing returns and refunds efficiently. Often there is ambiguity about the category of products that can be returned and those that cannot be returned. For example, it has to be clearly mentioned that innerwear or discounted clothes cannot be returned.
It is always a better strategy to be a good business that respects customers. Craft a clear and customer-friendly returns policy, streamline your returns management process to minimise time and costs, and focus on customer-centric processes.
9. Weak Cybersecurity
With the growing threat of crimes online, cybersecurity is a critical challenge in eCommerce. Businesses must prioritise robust security measures to protect customer data and prevent security breaches.
Establish strong cyber security by implementing SSL certificates, conducting regular security audits, and safeguarding customer data with encryption. Educate your staff on best security practices and be ever-vigilant in the face of potential cyber threats.
10. Few Payment Gateways
Offering diverse and secure payment options is vital for eCommerce success. The challenge lies in providing customers with a wide range of payment gateways that suit their preferences and instil trust.
Ensure user-friendly payment options: From credit cards to digital wallets, use the power of seamless transactions to match your customers’ preferences.
11. Lack of Customer Retention Strategy
Retaining customers is as important as acquiring new ones. Businesses must develop effective customer retention strategies to foster long-term relationships and drive repeat purchases.
The ideal strategy to retain customers is to offer personalised experiences, rewards programs, and exclusive offers. You can also use email marketing to stay connected with your customers.
12. Lack of Personalisation
When customers do not see recommendations, or there are wrong recommendations; they are likely to move away from the eCommerce seller.
Hence, personalisation, such as product recommendations, customised promotions, and greeting customers by name, will be necessary.
13. Lack of Cross-channel Integration
Poor inventory management creates dissatisfaction among customers. When they order a particular size, they expect to be delivered the same. If the inventory is wrongly managed, then it leads to dissatisfied customers and refunds.
Integrate different channels to provide a consistent brand experience. Synchronise inventory and order management, ensuring customers can effortlessly navigate between platforms with social media integration.
14. No Scope for Scaling
As an eCommerce business grows, scalability becomes a significant challenge. Increasing traffic and transaction volumes require businesses to continuously optimise their infrastructure.
Continuously optimise your infrastructure, upgrade server capacity, and virtualisation offer necessary solutions.
15. Weak Customer Service
Insufficient customer service can greatly hinder eCommerce companies and amplify the challenges they face in their operations.
To overcome this, you can establish multiple channels for customer support. Proactively engaging with customers and actively addressing their concerns will be highly beneficial and can contribute to building strong relationships and customer loyalty.
16. Lack of Data Analytics-driven Processes
Data analytics plays a crucial role in understanding customer behaviour, optimising marketing strategies, and improving business performance.
Data analytics track key performance indicators, analyse customer behaviour and gain insights into your business’s strengths and weaknesses.
17. Not Localised
Many eCommerce companies struggle to adapt their offerings to cater to the specific needs of local markets. As a result, they fail to attract customers and experience a lack of engagement from the online community, as there are no relevant products and services available.
To address this issue, businesses need to prioritise localisation efforts. This includes adapting website content and product descriptions to align with local regulatory requirements.
18. Lack of innovation
eCommerce sellers are likely to become stagnant and not attract new customers or retain customers if they do not innovate or offer exciting products to their customers.
A business that is the first adopter of new changes and is open to constant innovation to achieve customer satisfaction goals can drive growth. In eCommerce, innovation ensures you are aligned with industry developments, have the capability to explore emerging technologies and experiment with new marketing strategies.
19. Lack of Legal Considerations
Adherence to data protection and consumer protection laws is of utmost importance for eCommerce solution providers. Failure to comply can result in significant fines and legal repercussions.
For smooth eCommerce operations on your website, you should comply with the necessary data protection regulations applicable to your location. Seek counsel from legal experts to guide you through the maze.
20. Lack of Customer Engagement
With the abundance of choices and information available online, cutting through the noise and effectively delivering relevant and compelling content to engage customers becomes difficult.
Overcoming this challenge requires strategic planning, personalised experiences, cohesive messaging, transparent communication, reliable customer service, and the ability to adapt to changing customer needs.
E-Commerce in India
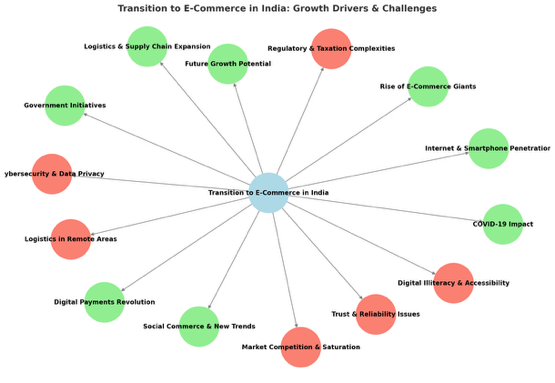
The transition to e-commerce in India has been a transformative journey, fueled by technological advancements, supportive government policies, and changing consumer behaviour. While the sector has witnessed rapid growth, it also faces unique challenges that need to be addressed for sustainable expansion.
Growth Drivers of E-Commerce in India
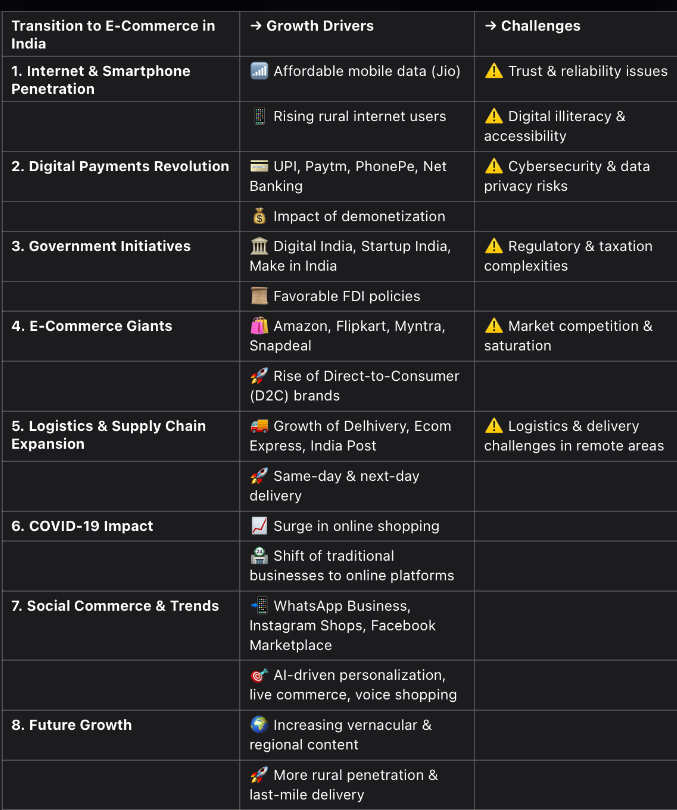
1. Internet & Smartphone Penetration
• The affordability of mobile data, led by Reliance Jio, has significantly boosted internet access across India.
• A rising number of rural internet users is expanding the consumer base for online shopping.
• Increased adoption of smartphones has made digital transactions and e-commerce more accessible.
2. Digital Payments Revolution
• The introduction of Unified Payments Interface (UPI), Paytm, PhonePe, and Net Banking has simplified online transactions.
• The demonetization drive (2016) pushed businesses and consumers toward digital payment solutions, accelerating e-commerce adoption.
3. Government Initiatives & Policies
• Programs like Digital India, Startup India, and Make in India have encouraged entrepreneurship and digital commerce.
• Favorable Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) policies have attracted global e-commerce giants to invest in India.
4. Rise of E-Commerce Giants
• Platforms such as Amazon, Flipkart, Myntra, Snapdeal, and Reliance JioMart have created a competitive marketplace.
• The emergence of Direct-to-Consumer (D2C) brands has allowed small businesses to sell online without intermediaries.
5. Logistics & Supply Chain Expansion
• Companies like Delhivery, Ecom Express, and India Post have expanded their reach, making deliveries faster and more efficient.
• Same-day and next-day delivery services have improved customer satisfaction and increased online shopping frequency.
6. Impact of COVID-19 on E-Commerce
• The pandemic led to a surge in online shopping, especially for essentials and groceries.
• Many traditional businesses shifted to online platforms, realizing the long-term benefits of digital commerce.
7. Social Commerce & Emerging Trends
• Platforms like WhatsApp Business, Instagram Shops, and Facebook Marketplace have enabled small businesses to sell directly to customers.
• AI-driven personalization, live commerce, and voice shopping are shaping the future of online retail.
8. Future Growth Potential
• Increased regional and vernacular content is making e-commerce more accessible to non-English-speaking users.
• Deeper rural penetration and enhancements in last-mile delivery are expanding the market.
• New-age startups and innovations in online retail are continuously redefining the e-commerce landscape.
Challenges Hindering E-Commerce Growth in India
1. Trust & Reliability Issues
• Many consumers are skeptical about product quality, authenticity, and return policies, leading to hesitation in online purchases.
2. Digital Illiteracy & Accessibility
• A significant portion of the population, particularly in rural areas, lacks digital literacy, preventing them from fully utilizing e-commerce platforms.
3. Logistics & Delivery Challenges in Remote Areas
• While urban delivery networks are robust, transportation and supply chain issues in rural areas remain a challenge.
4. Regulatory & Taxation Complexities
• The evolving taxation framework, such as GST policies, and compliance requirements pose difficulties for small businesses entering e-commerce.
5. Cybersecurity & Data Privacy Concerns
• The increasing number of cyber frauds, data breaches, and payment security risks make customers wary of online transactions.
6. Intense Market Competition & Saturation
• The dominance of established e-commerce players makes it challenging for small businesses and startups to gain visibility and market share
Indian readiness for E-Commerce
India has made significant strides in e-commerce readiness, driven by technological advancements, digital infrastructure, and policy support. However, certain challenges remain that need to be addressed for a seamless digital transition.
Future Prospects for E-Commerce in India
✅More Regional & Vernacular Support – Platforms adapting to Hindi, Tamil, Telugu, Marathi, and other regional languages
✅AI-Driven Personalisation – Improved customer experiences through recommendations & chatbots
✅Stronger Cybersecurity Measures – Stricter policies & technologies ensuring secure transactions
✅Growth in Rural E-Commerce – Expansion of digital literacy programs & logistics infrastructure

